Introduction
Mailchimp is an email marketing company founded by Ben Chestnut, Dan Kurzius, and Mark Armstrong.
What’s special about it?
If we look at the performance stats of this company, they are pretty impressive:
- As of 2021, Mailchimp has 80.81% market share in the email marketing industry.
- Mailchimp has 14 million paying users.
- Mailchimp has users in over 175 countries.
These are brilliant achievements for a company which started as a bootstrapped startup in 2001. But what grabbed our attention are 2 other facts about Mailchimp.
- Majority of Mailchimp users are small and mid-size companies.
- Majority of the Mailchimp users are newcomers in email marketing.
This is interesting and it is actually the reason behind Mailchimp’s success. Strategically Mailchimp made the brilliant move to woo small businesses and entrepreneurs because small businesses are greater in number and there is lower competition as all the competition among email marketing platforms is to bag big businesses.
Befriending Small Businesses
MailChimp uniquely positioned itself to serve small businesses because it intimately understood their needs and priorities. As a bootstrapped startup itself, MailChimp had walked in their customers’ shoes, experiencing firsthand the constraints of a small marketing budget and limited personnel.
This proximity enabled MailChimp to cater its platform and service offerings directly to those pain points – providing an affordable, customizable email marketing solution that empowered lean teams to create targeted campaigns with ease. While its better-funded competition focused on supporting enterprises, MailChimp optimized for the underserved small business market, rapidly rolling out features that solved real issues for those customers.
That keen customer empathy and scrappy, responsive approach allowed MailChimp to steadily gain market share. While the giants treated small businesses as an afterthought, MailChimp made them the core focus – earning loyalty through their dedication to customers’ real-world needs. Ultimately that commitment to genuinely helping small businesses succeed better than the rest is what fueled MailChimp’s rise.
So, the aim of our case study is to unveil how Mailchimp managed to do it. The mystery lies in its marketing technique.
Marketing Masterstrokes
Being a bootstrapped startup themselves Mailchimp understands the psychology of new entrepreneurs. From the very beginning the company maintained a non-corporate personality which is easily approachable.
They showcased their friendly nature with digestible content, affordable solutions and creative moments spotlighting real entrepreneur stories. Mailchimp continues capturing loyalty of budding businesses seeking marketing technology partners that intimately understand their grind through quirky yet meaningful campaigns.
1. From Paid to Freemium
In the beginning years Mailchimp’s email marketing platform operated on a paid-only model – every subscriber needed to input credit card details regardless of team size or email volume sent. But in 2009, the co-founders rethought this restrictive gating.
By introducing a free tier, Mailchimp allowed access to core features without upfront billing details…at least for sending up to 2000 messages. With this hybrid freemium approach established, the floodgates truly burst open!
Over the next 12 months, Mailchimp’s user base exploded nearly 6X from a modest 85,000 customers to over 450,000 subscribers. Support queries quintupled simultaneously. But more crucially, so did paying conversions once fledgling businesses experienced the platform’s potential to accelerate growth.
This pricing innovation, conceptualized to reduce barriers to product experience, transformed Mailchimp’s marketing funnel entirely. What had relied on outbound sales could now harness word-of-mouth and organic adoption fueled by an intoxicating free sample of the platform’s capabilities.
2. Relatable Real Business Owners
A core part of Mailchimp’s marketing showcases interviews and video testimonials from real-life small business owners who rely on their email marketing platform. From mom-and-pop bakeries sharing how custom templates drive cookie sales to online craft store owners explaining how automations nurture customers post-purchase, the entrepreneur journeys depicted resonate with their target niche. These authentic customer spotlights build trust and affinity with the small business community by highlighting relatable stories they connect with on an emotional level.
3. Quirky Advertisements
Mailchimp’s creative advertising campaigns not only pulled huge attention but also showed us that marketing can be done without following conventional ways.
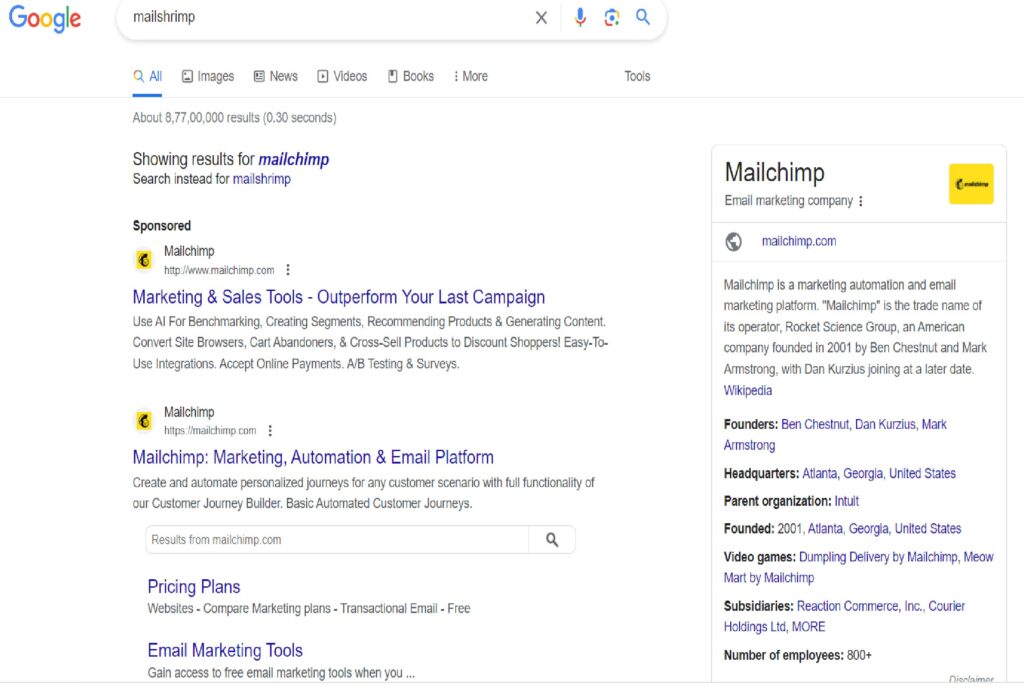
For example, the mispronunciation campaign.
These ambiguous audio and video advertisements allude to the company’s name in a subtle, tongue-in-cheek manner without overtly promoting the brand or any commercial offerings. These funny video advertisements were shown in different theaters as recently released films with names like KaleLimp,
JailBlimp,
MailShrimp, SnailPimp etc. These names didn’t make any sense and intrigued the audience to search for it on Google. Google identified these as a mispronounced word and came back with “Did you mean Mailchimp?”.
Bingo!
4. Humbled Startup Brand Imaging
Despite its global success serving millions of small businesses, Mailchimp maintains a humble, approachable personality through its whimsical mascot visuals, playful humor injected across digital campaigns, and self-deprecating captions at times.
This down-to-earth brand voice mirrors the early days of bootstrapping startups rather than an imposing Fortune 500 corporation that tiny niche ventures would feel intimidated by. From 404 pages to website imagery, they retain an unpretentious tone celebrating the scrappiness of small biz underdogs.
5. Snackable & Shareable Content
Mailchimp further retains learning and facilitates networking by creating bite-sized blog and social media posts whether about advanced email segmentation tactics or easy holiday promos any bootstrapper can implement.
Leveraging seasonal trends and current events through digestible infographics and witty posts injected with emojis has proven effective for wider organic reshares among interconnected small business communities on various networking platforms. This furthers perceptions of approachability for the brand.
Conclusion
Mail Chimp took a completely unconventional way to present themselves in the market. Mailchimp’s case demonstrates how even when facing better-funded competition, an intimate understanding of and laser focus on underserved customers’ needs, coupled with relatable branding and valuable content catered to their priorities, can earn market share through genuine user affinity and advocacy.
We frequently research and work on case studies which can serve as great pieces of learning for budding startups.
Subscribe to Ikana Business Review for more interesting case studies.